Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan
vol. 134, no.3, 2026
◆Full paper◆
Tracing nitridation reaction toward efficient production of oxynitride glasses as hosts for bright luminescence centers
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25148
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25148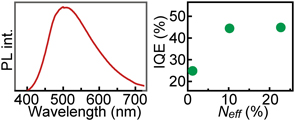
Xun Liu, Takeo Ohsawa, Noriko Saito, Kohsei Takahashi, Takashi Takeda, Kenzo Deguchi, Shinobu Ohki, Tetsuo Kishi, Tetsuji Yano, Hiroyo Segawa and Naoki Ohashi
87
Europium-doped oxynitride glass powder (Sr–Si–Al–O–N) was synthesized by a sol–gel method followed by ammonolysis to investigate the effect of the ammonolysis conditions on the structure and properties of the glass powder. In particular, the effect of the ammonia gas flow rate during nitridation was studied. The effective nitrogen concentration (Neff) in the obtained powder, analyzed by X-ray fluorescence, increased with an increase in the flow rate, and the results of X-ray photoemission, nuclear magnetic resonance, and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy measurements indicated that the population of Si–N bonds increased with an increase in Neff. However, the presence of hydrogen-terminated structures, such as –NHn, in the powder with high Neff was confirmed by FT-IR measurements. The presence of hydrogen-terminated structures, such as –Si–NHn, and the thermal stability of these hydrogen-related structures were further investigated by thermal analyses, including thermal desorption measurements, which suggested that hydrogen-terminated structures can be easily formed during the nitridation of the gel and that the formation of hydrogen-terminated structures inhibits the polymerization of the glass structures.
◆Express letters◆
Screening and mechanism analysis of negative thermal expansion in Bi0.85Ca0.15Fe0.85M0.15O3 (M: tetravalent cations) via machine learning force fields
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25162
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25162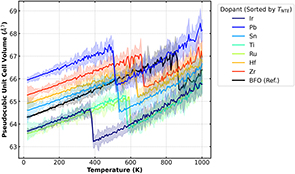
Shogo Wakazaki and Masaki Azuma
98
Negative thermal expansion (NTE) is a key property for achieving dimensional stability in advanced technologies, yet the discovery of new NTE materials is often hindered by the vast compositional space and the complexity of phase transition mechanisms. In this study, we applied large-scale molecular dynamics simulations using the Crystal Hamiltonian Graph Network (CHGNet), a pretrained universal machine learning force field (MLFF), to screen for NTE candidates in the Bi0.85Ca0.15Fe0.85M0.15O3 system (M = Ti, Zr, Sn, Hf, Ir, Pb, Ru). Our systematic simulations reveal that the co-substitution of Ca and tetravalent cations effectively modulates the phase stability of BiFeO3, with the transition temperature varying depending on the substituting element. Notably, the Ir-substituted compound exhibits a sharp volume-collapsing first-order phase transition at lower temperature (∼380 K) with a substitution level of 15 % in good agreement with the experimental result. These findings demonstrate that universal MLFFs are powerful tools for accelerating the exploration of functional materials and clarifying atomic-level mechanisms of complex phase transitions.
Synthesis of Cu fine particles via a solid–liquid reduction method using copper oxide
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25155
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25155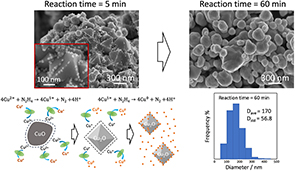
Yuto Ishida, Yamato Hayashi, Hirotsugu Takizawa and Minoru Ueshima
103
Copper fine particles were synthesized dispersant-free via a solid–liquid reduction method using copper oxide (CuO) and water as starting materials. Hydrazine monohydrate (N2H4·H2O) was used as a reducing agent and water as a dispersion medium, enabling the formation of Cu particles without generating harmful counterions or organic residues. Even under a high precursor concentration of 0.5 M, the addition of acetic acid and microwave heating promoted the reduction reaction, leading to the formation of fine and uniform Cu particles with an average diameter of 170 nm while suppressing oxidation and aggregation. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy analysis confirmed the absence of hazardous byproducts, although a small amount of acetohydrazide formed as a minor side product. Consequently, the obtained particles could be collected with a high yield (>90 %) simply by vacuum drying, without any washing process. This method significantly simplifies the Cu particle synthesis by eliminating washing and waste treatment steps, and is expected to serve as a low-cost, sustainable, and high-throughput manufacturing approach applicable to conductive inks and electronic materials.
◆Full papers◆
Enhanced deformability of TiC induced by off-stoichiometry
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25132
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25132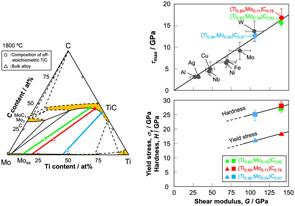
Shuntaro Ida, Eri Nakagawa, Florian Tropper, Takahito Ohmura and Kyosuke Yoshimi
110
NaCl-type MX compounds, comprising transition metals and nonmetals, exhibit excellent mechanical and thermal properties, making them suitable for high-performance applications such as cutting tools and aerospace components. However, their ductility is limited, particularly in stoichiometric forms such as TiC. Therefore, further investigation into improvement of their deformability and overall mechanical performance using off-stoichiometry and alloying is required. This study investigates the deformation behavior and mechanical properties of off-stoichiometric TiC formed in Mo–Ti–C ternary alloys via micropillar compression and nanoindentation tests. The activation of the {111}〈1−10〉 slip system and no fracture were observed after the plastic strain exceeded 5 %, indicating enhanced deformability due to the off-stoichiometry. The maximum shear stress required to initiate plastic deformation (τmax) was proportional to the shear modulus, a trend consistent with the ideal strength observed in various metals. This finding suggests that τmax corresponds to the shear stress necessary for the initial nucleation of dislocations. Both the yield stress and hardness increased with increasing shear modulus, indicating that these properties are governed by the Peierls stress in the large-strain regime. Overall, the findings demonstrate that the deformation in the ductility-enhanced off-stoichiometric TiC is dominated by dislocation motion and that its strength is primarily controlled by shear modulus.
Highly oriented ZnO varistors as ceramics with fine grains using tape casting and lamination, and the characteristics of anisotropy
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25101
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25101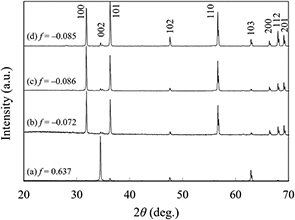
Yoshiko Higashi and Eiichi Koga
116
Highly c-axis oriented ZnO varistors are able to be successfully fabricated by industrial tape casting and lamination process, which use fine templated ZnO. They have Lotgering factor of 0.637 which is an index of degree of orientation, and are composed of isotropic fine grains of 2.2–3.0 µm. Significant variations are obtained in electrical properties of grain boundaries by crystalline orientation. Break down voltage per a grain boundary (Vgb) shows a decrease in perpendicular directions to c-axis alignment from those in parallel (−27 % in parallel to casting direction, −14 % in transverse), simultaneously with an increase in εr of relative permittivity. The orientational control is more likely to contribute enhancing the protection performance of ZnO based multilayer ceramic varistors.
Preparation and characterization of low-melting LiF–SnO–P2O5 glasses
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25145
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25145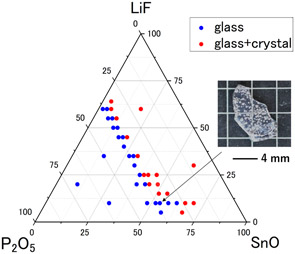
Hime Shibata, Kentaro Tabuchi, Riki Tokoro, Yuta Fujii, Akira Miura, Yuji Masubuchi and Kiyoharu Tadanaga
122
SnO–P2O5 glasses are known to have a low glass transition temperature (Tg) and can be vitrified in combination with metal oxides and halides. In this study, the glass-forming region in the LiF–SnO–P2O5 system was determined and the properties of the obtained glasses were characterized. The starting materials were melted at 400 °C, and the glass-forming regions in the LiF–SnO–P2O5 system were determined using X-ray diffraction and thermal analysis. The glass-forming region was restricted to P2O5 contents of at least 36 mol %, which is close to pyrophosphate, in LiF-rich compositions (≥30 mol %). On the other hand, the region extended to near the orthophosphate composition with high SnO content, such as 10LiF·62SnO·28P2O5 (mol %). The glass transition temperature of the prepared glasses ranged from around 150 to 210 °C. Sn K-edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectra of 10LiF·62SnO·28P2O5 (mol %) glass showed that the valence of Sn is predominantly Sn(II). The X-ray photoelectron spectra confirm the formation of P–F bonds in the glasses. A chemical durability test in the ambient atmosphere revealed that the glasses in the LiF–SnO–P2O5 system have relatively high chemical durability. AC impedance measurement showed the glass has ionic conductivity in the order of 10−8 S cm−1 at room temperature.
Photoluminescence of perovskite-type Cr3+-activated phosphors in the La–Al–Ti–O system
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25160
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25160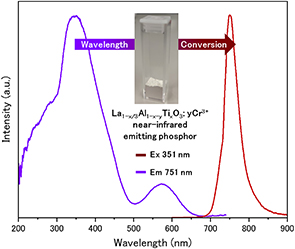
Akihiro Nakanishi, Takayuki Nakanishi, Naoto Hirosaki, Koji Morita and Takashi Takeda
128
Cr3+-activated near-infrared emitting phosphor has a potential application in plant growth and sensing technologies. Herein, we synthesized near-infrared emitting La1−x/3Al1−x−yTixO3:yCr3+ phosphor by a solid-state reaction. La1−x/3Al1−x−yTixO3:yCr3+ (x = 0.2, y = 0.003) showed the near-infrared emission at 751 nm with a full width at half-maximum of 41 nm under 351 nm excitation. The internal and external quantum efficiencies were 54.4 and 25.5 %, respectively. The luminescence intensities at 150 °C of the La1−x/3Al1−x−yTixO3:yCr3+ (x = 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3, y = 0.003) were 32, 17, and 3 % of those at room temperature, respectively. The thermal quenching effect strongly occurred with increasing the amount of Ti and it was related to the change in the absorbance edge of the host material La1−x/3Al1−x−yTixO3.
Tb:Gd9.33(SiO4)6O2 oxyapatite as an X-ray scintillator
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25165
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25165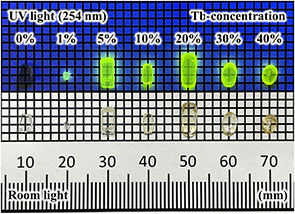
Ren Tsubouchi, Haruaki Ezawa, Hiroyuki Fukushima, Daisuke Nakauchi, Kenichi Watanabe, Takumi Kato, Noriaki Kawaguchi and Takayuki Yanagida
133
Gd9.33−xTbx(SiO4)6O2 (x = 0, 0.093, 0.467, 0.933, 1.866, 2.799, 3.732) oxyapatite single crystals were grown by the floating zone method, and their photoluminescence (PL) and scintillation properties were systematically investigated. Under UV and X-ray excitation, the samples exhibited emission peaks due to the 4f–4f transitions of Gd3+ and Tb3+. The decay times were on the milliseconds scale, consistent with Tb3+ emission. The PL quantum yields of the 1–30 % Tb-doped samples were approximately 70 %, and the light yield of the 10 % Tb-doped sample was 15400 photons/MeV, as calculated from the pulse height spectra under 137Cs γ-ray irradiation.
Surface structural change on pellets of calcium ethyl phosphate in biomimetic solutions: Effects of carbonate concentrations
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25142
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25142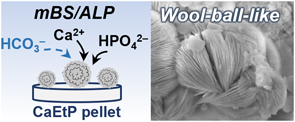
Wanyu Dong, Yuko Matsukawa, Taishi Yokoi, Kazumasa Suzuki and Chikara Ohtsuki
140
Hydroxyapatite (HAp) with similarity in natural bone mineral is called bone-like apatite (BAp), and the formation of BAp on material surfaces in the body environment substantially contributes to materials to make bonding to living bone. It is proposed that designed materials, namely salts of calcium and phosphate esters (SCPEs), possess the property of enhancing BAp formation in simulated body fluid (SBF) modified with alkaline phosphatase (ALP). Such materials are called bioresponsive ceramics. The crystalline phase of BAp is generally identified as HAp by X-ray diffraction analysis. Since several-types of SBF have been reported, in this study, HAp formation on calcium ethyl phosphate (CaEtP) pellets, which is one of SCPEs, was examined in the solutions mimicking SBF, that is, modified biomimetic solution (mBS) and evolved biomimetic solution (eBS). The critical difference between these solutions and conventional SBF is carbonic acid concentrations in the solutions. It was found that capability of HAp formation of CaEtP pellets in mBS and eBS was lower than that in mBS and eBS containing ALP. The morphology of the HAp formed on the pellets was distinctive in mBS and eBS containing ALP: i.e., formation of wool-ball-like shaped particles in mBS containing ALP, while formation of fine spherical particles in eBS containing ALP. These differences, namely nucleation, crystal growth and morphology, are likely governed by concentrations of carbonate ion species in the reaction solution. It can be concluded that controlling the concentration of carbonate ions in the biomimetic solutions enables controlling the formation behavior of HAp as well as its morphology. These findings provide basic knowledge about nucleation and crystal growth of HAp in biomimetic solutions as well as basic understanding of the reactivity on bioresponsive ceramics.
Release of phosphate and phosphonate from phenylphosphonate-modified zirconium phosphate in biomimetic solutions
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25147
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25147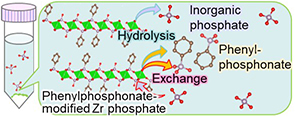
Ryohei Kozaki, Yuko Matsukawa, Kazumasa Suzuki, Jin Nakamura and Chikara Ohtsuki
148
In this study, the release of phosphorus oxyacid species from organically modified layered zirconium phosphate was investigated. Zirconium phosphate was modified by partially incorporating phenylphosphonate by heating a mixture of phosphoric acid and phenylphosphonic acid under reflux. Characterization by powder X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis confirmed that approximately 50 % of the phosphate groups in the zirconium phosphate framework were successfully replaced by phenyl groups. Upon immersion in Tris-hydrochloric acid buffer for 168 h, both inorganic phosphate and phenylphosphonate were released. In contrast, in phosphate-buffered saline, phenylphosphonate was eluted while inorganic phosphate from the solution was incorporated into the material. These results suggest that zirconium phosphate modified with phenylphosphonate can serve as a potential material for imparting phosphorus oxyacid-based drug-releasing functionality to zirconia-based dental materials.
Preparation of phosphate glasses via ethanol-based liquid-phase method
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25156
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25156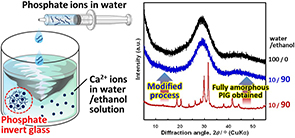
Hayato Asano, Akiko Obata, Makoto Sakurai, Fukue Nagata and Sungho Lee
154
Phosphate invert glasses (PIGs) are promising biomaterials because of their ability to release ions and their biocompatibility. Using water-based liquid-phase methods, PIGs can be synthesized at ambient temperature and pressure. However, the compositional range is limited owing to the hydrolysis of water-sensitive raw materials, such as NbCl5 and TaCl5, which produce insoluble hydroxides and oxides. Thus, the incorporation of tantalum (Ta) and niobium (Nb) into the PIG network structure is difficult, despite their ability to enhance chemical durability and introduce biological functionalities. In this work, an ethanol-based liquid-phase method was developed to prepare PIGs for certain water-sensitive raw materials. The ethanol content in the method is significantly related to the glass network structure and crystallization behavior. PIGs without crystalline phases were obtained with ethanol content up to 50 %, whereas higher ethanol content led to partial crystallization of K2CaP2O7. Modifying the process can suppress crystallization at the high ethanol content, allowing the preparation of PIGs without crystalline phases. Thus, the proposed method can be used to prepare crystallization-free PIGs containing water-sensitive elements.
Microstructure of hydrated Ca3SiO5 and interfacial transition zone characterized by X-ray computed nano-tomography
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25138
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25138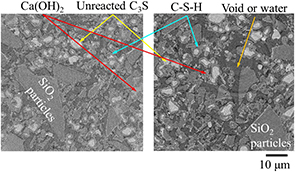
Shin Tajima, Hideto Takekawa, Daigo Setoyama and Satoshi Yamaguchi
161
This study investigates the microstructure of hydrated Ca3SiO5 (C3S) and the interfacial transition zone (ITZ) between an aggregate and hydrated C3S, both of which critically influence the properties of concrete. Because cementitious materials are normally wet, it is difficult to observe their microstructure using scanning electron microscopy. Therefore, the microstructure was examined using X-ray computed nano-tomography at SPring-8 (with a spatial resolution limit of ∼100 nm), which enables the nondestructive imaging of internal structures in the atmosphere. X-ray computed nano-tomography allows observation of the microstructure in the wet state, where residual water is present and hydration products remain intact. The analyses revealed the formation of a calcium silicate hydrate, while Ca(OH)2 particles with diameters of several micrometers were not detected during the initial stage of hydration. At this stage, Ca(OH)2 likely dissolved in water in a supersaturated state with respect to Ca2+ ions, or alternatively, Ca(OH)2 nanoparticles (<100 nm) may be dispersed in the aqueous phase. In the hydrated mixture of C3S and SiO2 (aggregate), Ca(OH)2 particles with diameters of several micrometers were not present at the interface between C3S and SiO2 (ITZ) but were located around the hydrated C3S particles, a phenomenon that differs from previously reported observations. These findings contribute to the understanding of the formation behavior of the calcium silicate hydrate and microstructure of the ITZ.
◆Technical report◆
Preparation and characterization of alumina granules via tumbling and agitation granulation
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25139
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25139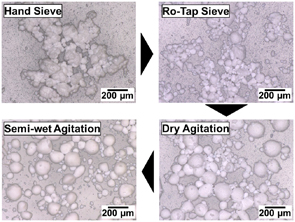
Naoki Kondo, Akihiro Shimamura and Mikinori Hotta
168
Granulation of alumina powder was performed, and the characteristics of the resulting granules and the sintered bodies produced from them were evaluated. The granulation processes were conducted under the following conditions: hand sieving (HS), sieving using a rotating and tapping shaker (Ro-Tap sieving, RTS) which involves a tumbling motion; dry agitation granulation using a high-shear mixer (AD); and semi-wet agitation granulation with binder addition (AB). The granulation effect increased progressively in the order of HS, RTS, AD, and AB. As the granulation effect increased, the granules became larger and more spherical, and their size distribution became narrower with a sharper peak. The loose bulk density increased and the angle of repose decreased, whereas the tapped bulk density showed no significant change due to the collapse of the granules. Although the strength of the granules increased with the progression of granulation, the strength of the sintered bodies decreased. This phenomenon is considered to result from the stronger granules being less prone to collapse during compaction, which led to the formation of residual pores between granules in the green bodies. These pores subsequently became defects in the sintered bodies, which reduced their strength.
◆Notes◆
Preparation and evaluation of antiviral activity of Zn-doped CeO2 under dark and visible-light irradiation
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25151
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25151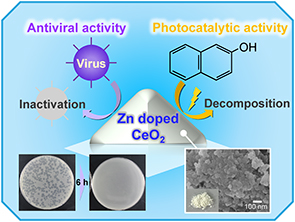
Mizuki Tomaru, Yasuhide Mochizuki, Toshihiro Isobe, Keiichi Kobayashi, Takeshi Nagai, Hitoshi Ishiguro and Akira Nakajima
174
After Zn-doped CeO2 (CZnO) was synthesized using a hydrothermal method, its antiviral activity was evaluated under dark and visible-light conditions. The obtained sample was a white, single-phase powder with a fluorite-type crystal structure. Compared with undoped CeO2, CZnO exhibited a smaller lattice constant and a larger specific surface area. Its antiviral activity was assessed in accordance with ISO standards using an enveloped virus (bacteriophage Φ6) and a non-enveloped virus (bacteriophage Qβ). Even in the dark, CZnO showed distinct antiviral activity against both viruses, with stronger effects observed for Φ6. Detailed analyses indicated that particle size, released ions, and surface charge contributed to the antiviral behavior under dark conditions. Under visible-light irradiation, the antiviral performance of CZnO was enhanced further, with a particularly pronounced effect found against Qβ. This enhancement is attributed to photocatalytic effects: Zn doping was found to narrow the band gap and increase photon absorption. These findings indicate CZnO as a novel inorganic antiviral material capable of exhibiting antiviral activity under both dark and visible-light conditions without the need for any co-catalyst or rare-earth dopant.
Preparation and thermo-responsive properties of poly(acrylamide-co-acrylonitrile)/layered double hydroxide composite gas barrier membrane
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25157
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.25157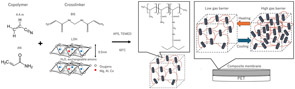
Shingo Ikeda, Tomohiro Murakami and Koji Kuraoka
182
Thermo-responsive gas barrier membranes were fabricated using acrylamide–acrylonitrile copolymers and layered double hydroxides. The membranes exhibited temperature-dependent behavior, showing enhanced water vapor barrier properties below 40 °C and reduced performance at 50 °C. Such characteristics are attractive for packaging applications in logistics, where fluctuating temperatures can affect perishable products. By providing stronger barrier properties at lower temperatures and allowing increased permeability at higher temperatures, these membranes may help mitigate condensation-related damage during transportation. FT-IR analysis revealed a slight low-wavenumber shift in the amide absorption peaks upon LDH incorporation, suggesting molecular-level interactions between the copolymer matrix and the inorganic layers. These findings indicate that combining UCST-type copolymers with LDH fillers offers a promising approach for developing membranes with tunable gas barrier performance for future smart packaging systems.
◆Announcement◆
Call for a Guest Editor for the Feature
 https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.134.A3-1
https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.134.A3-1A3-1
© Copyright by The Ceramic Society of Japan

